Understanding Transfer Cases in Heavy Equipment: Function, Components, and Warning Signs
Transfer cases are a fundamental component found in various machines, from standard 4x4 trucks to massive off-road haulers. They play a crucial role in dividing power from the transmission and distributing it to each of the powered axles.
What is a Transfer Case?
A transfer case serves as a critical power distribution hub in vehicles with multiple powered axles. It ensures that the appropriate amount of power is delivered to each axle, enabling efficient movement and control. This power distribution can be achieved through either gears or a chain drive system, each offering distinct advantages:
-
Chain Drive: Chain-driven transfer cases are favored for their reduced weight and noise levels. They provide a seamless power transition to the axles, contributing to smoother operations.
-
Gears: Gear-driven transfer cases are prevalent in most heavy equipment due to their higher torque capacity, enhanced durability, and reliability. These robust transfer cases can withstand the demands of heavy-duty applications.
How Does It Work?
In machines with a single powered axle, a transfer case may not be required. The driveshaft connects directly from the transmission to the axle, efficiently transmitting power. However, in equipment with multiple powered axles, a transfer case becomes essential to distribute power effectively.
Heavy equipment transfer cases often incorporate one or more sets of low-range gears. These gears provide an additional torque boost when navigating challenging terrains or carrying heavy loads, ensuring optimal performance.
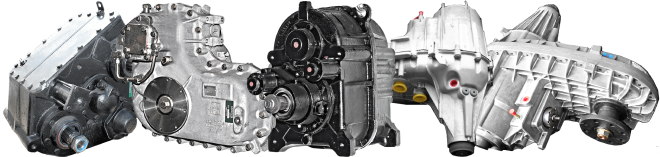
Components of a Transfer Case
A transfer case comprises several integral components that work harmoniously to execute its function:
-
Bearings: Bearings facilitate smooth rotation of the various components within the transfer case.
-
Gears: Gears are responsible for transferring power and torque to the axles.
-
Shafts: Shafts transmit rotational force between different sections of the transfer case.
-
Flanges: Flanges connect the transfer case to the powered axles via driveshafts.
-
Housing: The transfer case housing encases and protects the internal components.
-
Seals, Gaskets, and O-Rings: These components prevent fluid leaks and maintain a proper seal within the transfer case.
Location and Placement
The transfer case is strategically positioned between the transmission and the powered axles. It is seamlessly integrated into the drivetrain and functions as a central hub for power distribution. Each axle is connected to the transfer case via a driveshaft, enabling synchronized movement.
Warning Signs of a Failing Transfer Case
Detecting issues with the transfer case is essential to prevent operational disruptions and potential damage. Watch out for the following warning signs:
-
Grinding or Humming Sounds: Unusual noises emanating from beneath the machine, such as grinding or humming, may indicate a transfer case problem.
-
Erratic Movement: If you experience erratic movement, such as slipping or lurching, it could be a sign of an underlying transfer case issue affecting power distribution.
Need a transfer case for your equipment? Click below to get a quote today!